21. Appendix D SEGGER SystemView integration instructions¶
SEGGER SystemView is a real-time recording and visualization tool that reveals the true runtime behavior of an application. To enable SystemView, follow the instructions below.
Configuring SmartSnippets™ Studio projects to support SystemView:
To enable SystemView for a specific build configuration of any SmartSnippets™ Studio project, configure the project to build SystemView’s source files and include header file directories:
- Select a project which has the
OS_FREERTOSdefinition enabled. Bare metal projects are currently not supported. - Right click project’s “sdk” subfolder and go to
New -> Folder
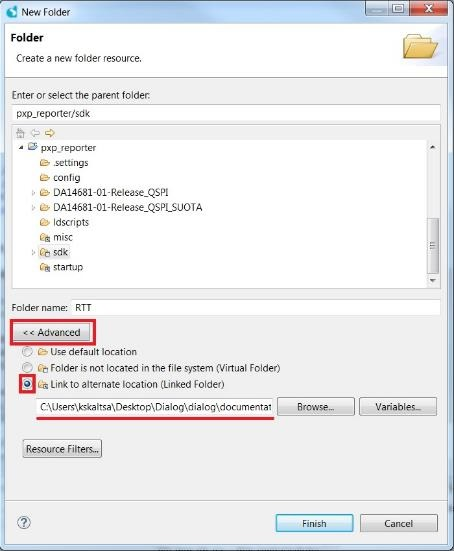
- In the pop-up window select:
Advanced -> "Link to alternate location" -> Browse…and select the<sdk_root_directory>/sdk/middleware/segger_toolsfolder as shown in Figure 94.
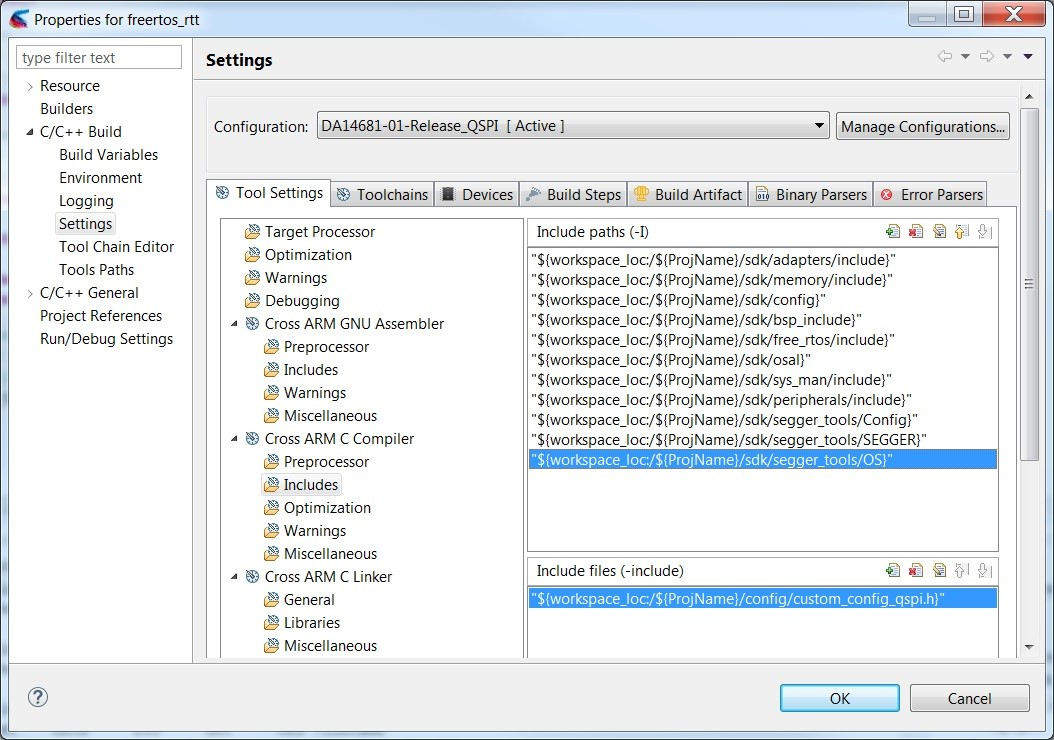
- Right click project’s name and go to
Properties -> C/C++ Build -> Settings -> Tool Settings -> Cross ARM C Compiler -> Includes -> Include Paths(see Figure 95), add the following Workspace folders and click apply:
${workspace_loc:/${ProjName}/sdk/segger_tools/Config}
${workspace_loc:/${ProjName}/sdk/segger_tools/OS}
${workspace_loc:/${ProjName}/sdk/segger_tools/SEGGER}
- Open the project’s
config/custom_config_*.hfile and add Code 44 to add and enable the System View configuration:
#define dg_configSYSTEMVIEW (1)
Note
that configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE should be increased by``dg_configSYSTEMVIEW_STACK_OVERHEAD`` bytes for each system task. For example, if there are 8 system tasks, configTOTAL_HEAP_SIZE should be increased by: (8 * dg_configSYSTEMVIEW_STACK_OVERHEAD) bytes.
- To call
SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Conf()from application add Code 45. A good place to do this is insidesystem_init()after the configuration of system clocks:
#if dg_configSYSTEMVIEW
SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Conf();
#endif
- Build and download the application image to DA1468x. Then run the application either by pressing the Reset Button (Release Build) or by start debugging the application.
- To disable SystemView, set
dg_configSYSTEMVIEWto0and rebuild the application.
Running SystemView on the Host:
- Start the Segger System View application from SmartSnippets™.
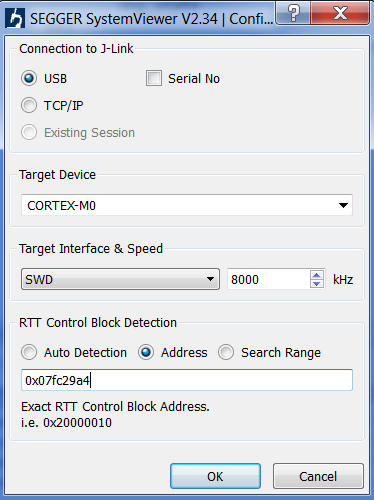
- Configure the SEGGER System View as shown in Figure 97.
Note
that the address for the RTT Control Block Detection is located
in application’s .map file. For example, for PXP reporter the .map
file is located at pxp_reporter/DA14681-01-Release_QSPI. Press
Ctrl+F and search the address of the _SEGGER_RTT variable.
- On the main SystemView window, press the upper right “Start Recording Button” button.
- One can Stop and Restart the recording at any time using the buttons from SystemView PC Application.
Additional information:
- The processing overhead of SystemView is not negligible and can potentially affect system dynamics or cause assertions due to the delays inserted from ISR monitoring. To minimize the impact on time critical ISRs there are some configuration options that allow the user to enable/disable the monitoring of certain aspects of the system, as shown below:
/**
* Enable/Disable SystemView monitoring for BLE related ISRs (BLE_GEN_Handler / BLE_WAKEUP_LP_Handler).
*/
#ifndef dg_configSYSTEMVIEW_MONITOR_BLE_ISR
#define dg_configSYSTEMVIEW_MONITOR_BLE_ISR (1)
#endif
/**
*Enable/Disable SystemView monitoring for CPM related ISRs (SWTIM1_Handler / WKUP_GPIO_Handler).
*/
#ifndef dg_configSYSTEMVIEW_MONITOR_CPM_ISR
#define dg_configSYSTEMVIEW_MONITOR_CPM_ISR (1)
#endif
/**
*Enable/Disable SystemView monitoring for USB related ISRs (USB_Handler / VBUS_Handler).
*/
#ifndef dg_configSYSTEMVIEW_MONITOR_USB_ISR
#define dg_configSYSTEMVIEW_MONITOR_USB_ISR (1)
#endif
In applications with heavy IRQ usage it is possible that the currently used 2kb RTT buffer cannot hold all the monitored events and this may cause RTT overflows which simple means that some events are lost. The number of lost events is visible in the System View GUI RTT overflows property.
To avoid this SEGGER suggest:
- Minimize the interactions of the debugger with J-Link while the target is running. (i.e. disable live watches)
- Select a higher interface speed in all instances connected to J-Link. (i.e. The debugger and System Viewer)
- Choose a larger buffer for System View. (1 - 4 kByte)
- Run System Viewer stand-alone without a debugger.
System View uses sdk’s RTC, which is clocked by one of the LP clocks. For example, if the LP clock is
XTAL32Keach timer tic corresponds to ~31us. Events that last less than 30us will be visualized as events that last 31us.Application/Device name can be set in
SEGGER_SYSVIEW_Config_FreeRTOS.cSYSVIEW_APP_NAME/SYSVIEW_DEVICE_NAMEdefinitions. At the same file function_cbSendSystemDesc()is located which sends comma separated IRQ names to the Host PC. Because the internal used buffer is only 128 bytes, not all IRQs are named there. One could use multipleSEGGER_SYSVIEW_SendSysDesc()calls to name all IRQs but this means more processing requirements. It is recommended to leave just one packet there.Memory overhead is 2Kb RAM for RTT buffers, 256 bytes heap for every thread, 256 bytes stack for the shared IRQ stack and ~5Kb rom.
It is possible to redirect
printfmessages on SystemView’s host window:- if
CONFIG_RETARGETis defined, messages go to UART - if
CONFIG_RTTis defined, messages go to RTT - if
CONFIG_NO_PRINTis defined, messages are discarded - If nothing of the above is defined, but the
dg_configSYSTEMVIEWis enabled, messages go to System View’s GUI terminal.
- if
Currently System View supports only integer variables, so %s strings are not printed properly. printf using SystemView inserts delays (because of the temporary disabled IRQs) that may trigger assertions so it is not recommended to be used.